Written by Adam Bronfin
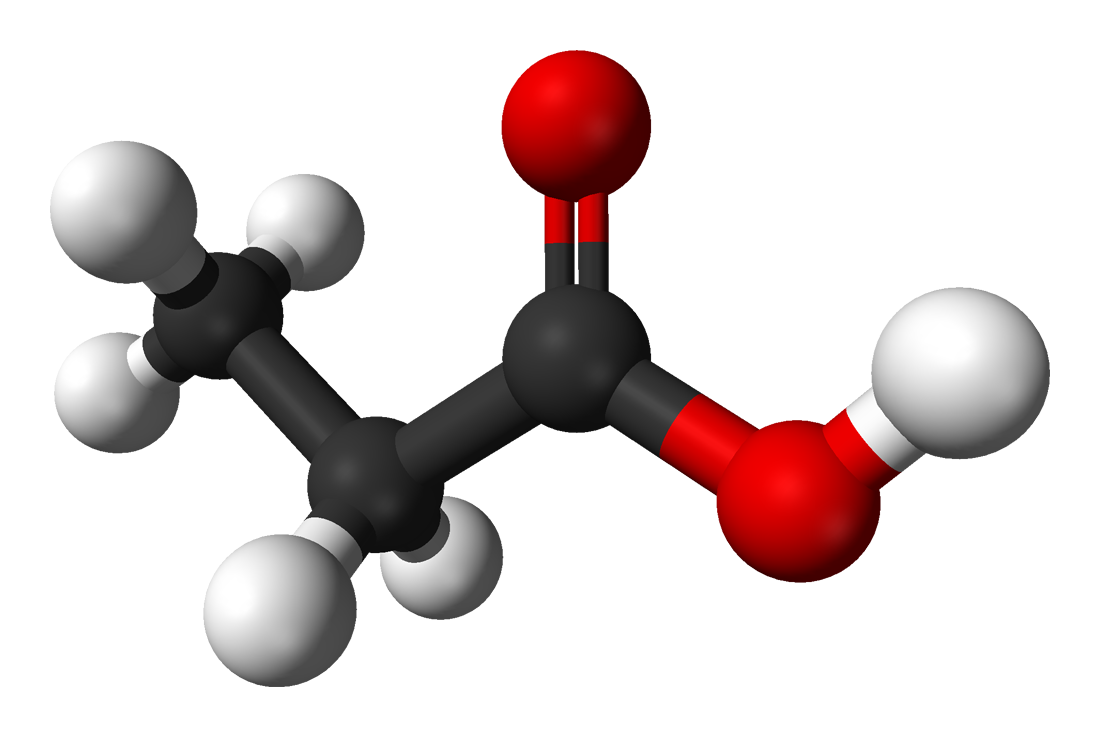
In studying food additives, the first thing you need to know is that whether we mention
calcium propionate, calcium propanoate or propionic acid, we are talking about the same
thing. Because as I mentioned before calcium propionate is the calcium salt of propionic
acid.
Whether the molecule exists in solution as calcium propionate or as propionic acid
depends on the pH of the solution. At lower pH values, the molecule exists as propionic
acid, and higher pH values it exists as calcium propionate. The pKa of propionic acid about 4.9, so at a pH values lower than this, the compound is mostly in an undissociated state,
while above this it’s mostly in a dissociated state.
The way calcium propionate affects food is thought to be caused mostly by the molecule in its undissociated state, which means that the lower the pH, the more effective the
preservative will be. The mechanism of action is thought to be because the undissociated
molecule is lipophilic (lipid loving) and readily dissolves into cell membranes. Once the
molecule is there, it may interfere with the membranes permeability. Anything that disrupts membrane permeability makes it hard for cells to function normally.



No comments:
Post a Comment